Fungal infections have “significantly increased” among hospital patients during the COVID pandemic, according to the World Health Organization, as it released its first-ever list of fungi that pose the greatest threat to human health.
The WHO reportdescribing fungal “priority pathogens,” warned that some strains are becoming increasingly drug-resistant and becoming more common.
There are only four treatments, and very few new options are in development, the report said.
Climate change means that the distribution and geographic range of pathogens is expanding, while resistance is partly driven by the overuse of antifungals in agriculture, the WHO said.
People at greatest risk of invasive fungal infections include cancer patients, HIV/AIDS patients, organ transplant recipients, chronic respiratory disease and post-primary tuberculosis infection, he warns.
The WHO list of priority fungal pathogens contains 19 fungi that pose the greatest threat to public health.
The list divides pathogens into three categories – critical, high and medium priority – based on their potential impact and data on their persistence risk.
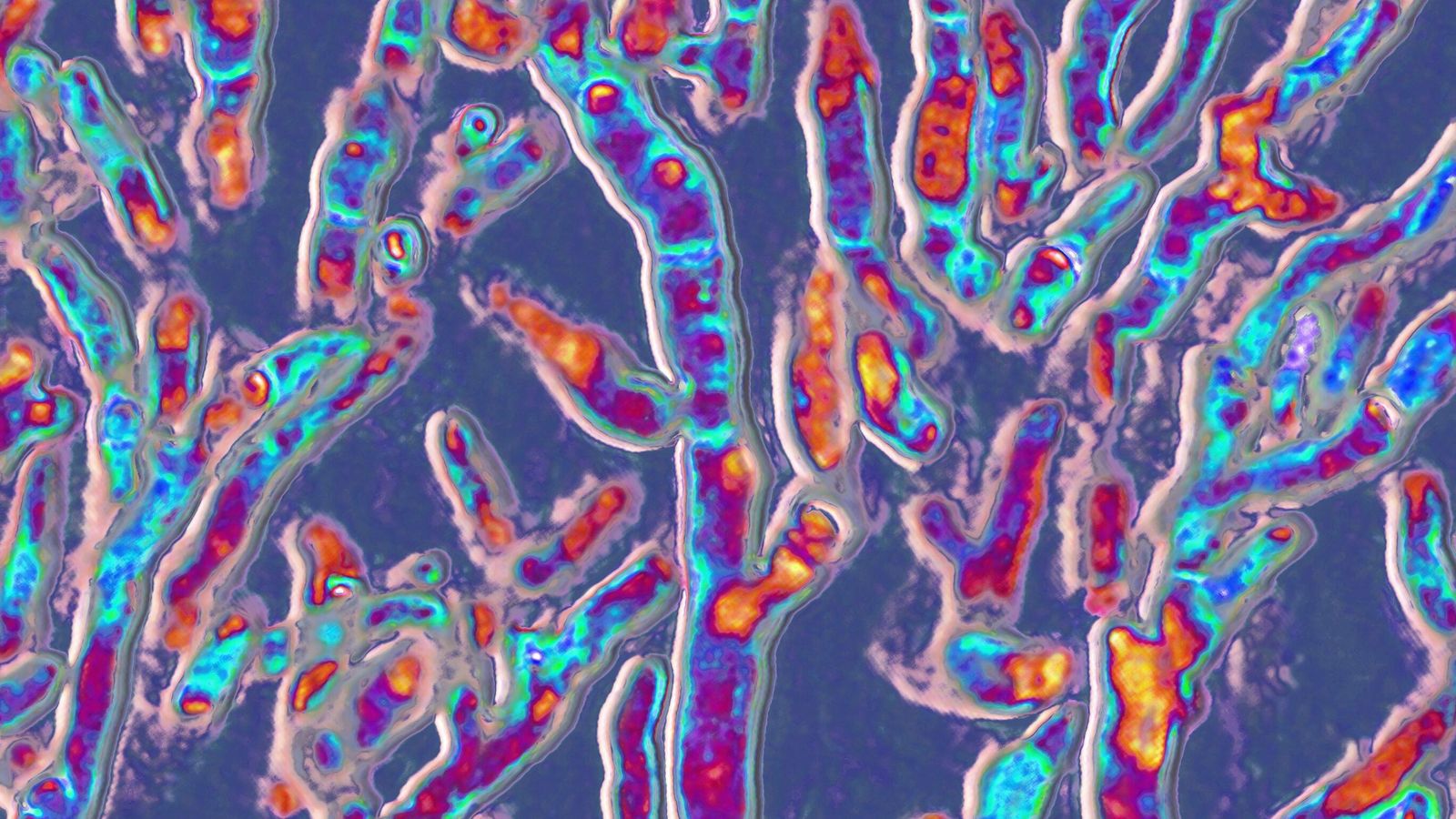
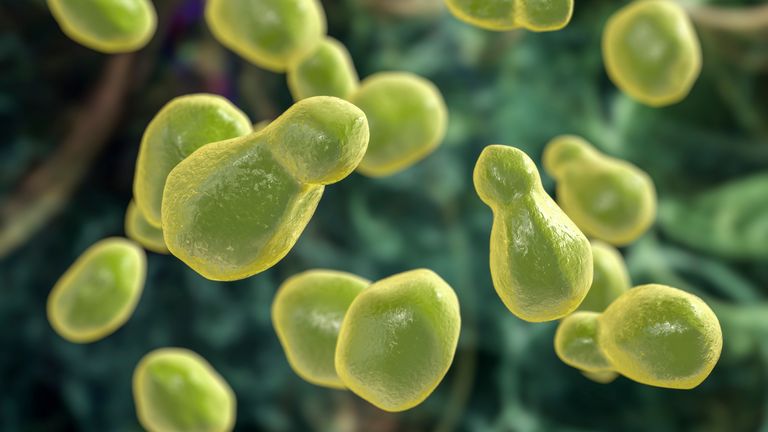
Candida auris, Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida albicans are classified in the highest-rated “critical” group.
Candida auris is highly drug resistant and has caused a number of outbreaks in hospitals around the world. This is a new fungal infection that also causes infections mainly in immunocompromised people.
It is a globally distributed pathogenic yeast that can cause invasive candidiasis of the blood (candidemia), heart, central nervous system, eyes, bones and internal organs.
The overall mortality risk for invasive candidiasis with Candida auris ranged from 29% to 53%.
Cryptococcus neoformans is an infection that usually affects people with compromised immune systems, such as HIV or cancer, and can cause meningitis.
Cryptococcosis caused by Cryptococcus neoformans can be life-threatening with a 41% to 61% mortality risk and cause complications such as blindness and kidney failure.
Aspergillus fumigatus is a common mold that is widely distributed in the environment in people’s homes and outdoors. It often causes lung problems in people with existing lung problems and can cause asthma-like conditions, pulmonary fibrosis, or a non-cancerous tumor.
Candida albicans is the main cause of thrush, which is a common and unpleasant disease. However, in people with weakened immune systems, it can cause a number of serious illnesses, including meningitis and septicemia.
A global public health concern
Clinical trials aimed at reducing morbidity and mortality are needed, the report notes.
The number of fungal infections and how far they spread around the world may be increasing due to climate change and growth in international travel and trade, WHO said.
However, due to the scarcity of quality data on fungal infections and the lack of attention given to them, the magnitude of the threat of fungal diseases and their resistance to treatment is unknown.
WHO has called on governments and researchers to step up their response to 19 mushrooms on the list.
“Coming from the shadow of the pandemic of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial drugs, fungal infections are increasing and becoming more resistant to treatment, becoming a public health problem worldwide,” said the organization’s Dr. Hanan Balkhi.
https://news.sky.com/story/fungal-infections-increased-significantly-during-covid-pandemic-as-who-reveals-health-threatening-fungi-list-12730791